Waste resource utilization is a crucial measure for implementing the concept of green development. The screening process, as a core step in waste classification and resource recovery, requires various specialized equipment for precise sorting. If ferromagnetic materials mixed in the waste are not effectively separated, it will not only affect the efficiency of subsequent processing but also potentially cause equipment malfunctions and safety hazards. Magnetic separators, based on the core principle of magnetic separation, are suitable for various waste screening scenarios (including aged waste, municipal solid waste, and construction waste), achieving efficient recovery of ferromagnetic materials and removal of impurities. They combine resource recovery value with process optimization, making them an indispensable key equipment in waste screening systems.
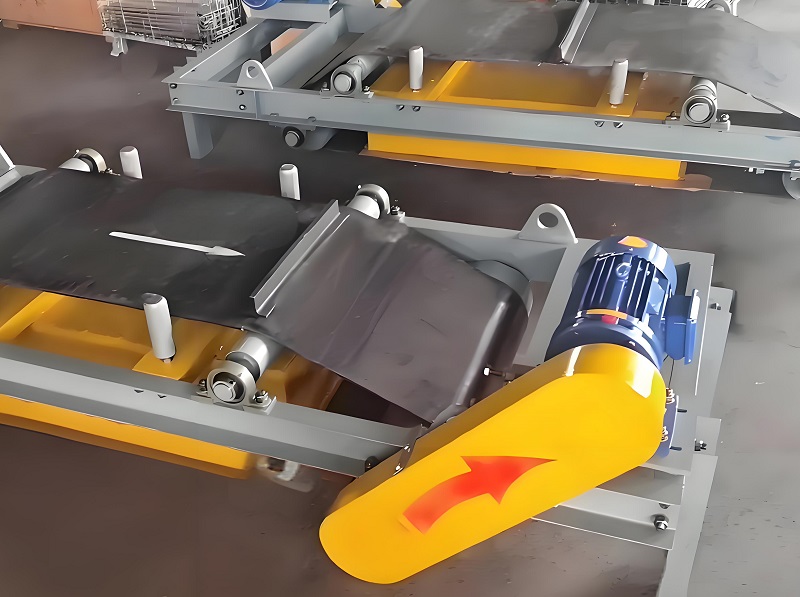

The core value of magnetic separators lies in the precise separation of ferromagnetic materials, solving the problem of impurity interference and ensuring the safe and stable operation of subsequent screening and processing stages. Waste commonly contains ferromagnetic impurities such as nails, wires, scrap rebar, sheet metal, and magnetic metal fragments. These materials have high hardness, and if they enter subsequent processes such as crushing, grinding, and incineration, they will severely wear down equipment components, leading to frequent replacement of vulnerable parts such as crusher hammers and screens, increasing equipment maintenance costs. At the same time, metal impurities may entangle equipment shafts, causing downtime and affecting the continuity of waste processing. Magnetic separators generate a stable magnetic field; when waste materials pass through the magnetic field area, ferromagnetic materials are attracted by the magnetic field and precisely separated from non-magnetic materials, fundamentally avoiding damage to subsequent equipment caused by metal impurities and ensuring the efficient operation of the waste treatment production line.
In waste resource recovery, magnetic separators play a crucial role in recovering magnetic resources, improving resource utilization, and creating considerable economic benefits. Ferromagnetic metals are recyclable resources. Scrap iron and steel from waste, after separation and recovery, can be processed through crushing and smelting to be remanufactured into metal raw materials, replacing some primary mineral resources and reducing the ecological damage caused by mining, thus aligning with the needs of a circular economy. Compared with traditional manual sorting, magnetic separators require no manual intervention, enabling continuous and automated sorting, significantly improving recovery efficiency, reducing the labor intensity and costs of manual sorting, and avoiding resource waste caused by omissions in manual sorting. According to industry data, waste treatment lines equipped with magnetic separators can achieve a recovery rate of over 95% for ferromagnetic materials. Large-scale recovery can bring stable additional revenue to enterprises, achieving a win-win situation for both environmental protection and economic benefits.
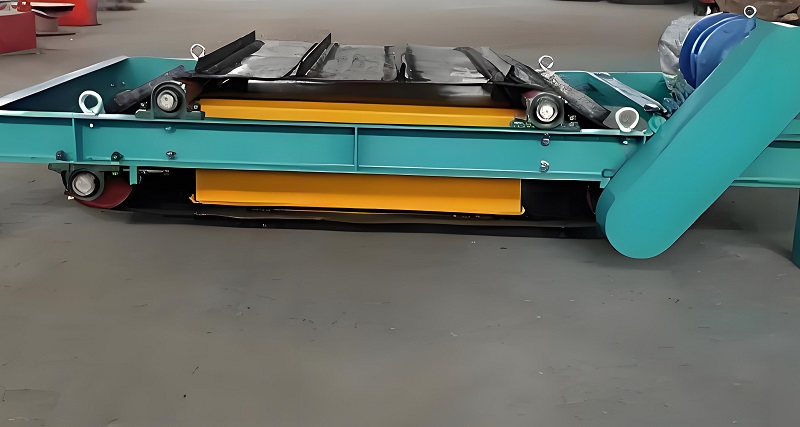

Magnetic separators are adaptable to various waste screening scenarios, flexibly adjusting to different material characteristics, improving sorting versatility and adaptability. Waste is complex, with significant differences in composition, humidity, and particle size. Whether it's dry household waste, sticky aged waste, or construction waste mixed with bricks and stones, magnetic separators can achieve efficient separation by adjusting the magnetic field strength and material conveying speed. For magnetic materials wrapped in humus in aged waste, the magnetic separator can enhance the magnetic field strength to overcome material adhesion interference and effectively adsorb magnetic materials; for small magnetic metal fragments, the conveying structure can be optimized to extend the material's residence time in the magnetic field, preventing missed sorting. Currently, magnetic separators are widely used in household waste transfer stations, aged waste excavation and disposal, and waste incineration pretreatment, becoming a highly versatile auxiliary equipment for waste screening.
Magnetic separators can also optimize subsequent disposal processes, reducing environmental risks and disposal costs, and contributing to harmless waste disposal. In the waste incineration process, if ferromagnetic metals are mixed in, high-temperature molten metal particles will form during combustion, potentially damaging the furnace wall and increasing the emission of heavy metal pollutants in the flue gas, exacerbating environmental treatment pressure; in the landfill process, metal impurities buried for a long time will affect landfill compaction operations, and some metals may be leached by leachate, causing soil and groundwater pollution. Separating ferromagnetic materials in advance with magnetic separators can improve the uniformity of incinerated materials, reduce heavy metal emissions, and lower environmental treatment costs; at the same time, it reduces metal impurities in landfill waste, optimizes landfill compaction effects, extends the service life of landfills, and balances the needs of harmless disposal and environmental emission reduction. Magnetic separators, by precisely separating magnetic impurities, recovering usable magnetic resources, adapting to various sorting scenarios, and optimizing subsequent disposal processes, have become a core auxiliary equipment in waste sorting systems. They not only mitigate safety hazards caused by metal impurities but also enhance the value of resource recovery, contributing to the goals of waste reduction, harmless treatment, and resource utilization. With the intelligent upgrading of waste disposal, magnetic separators will optimize their performance through the integration of automated control technology, further improving sorting accuracy and efficiency. In the future, their application in various waste disposal scenarios will become even more widespread, providing strong support for green and low-carbon development.