In the vast system of waste management, waste screening is a crucial link. Through various screening machines, waste can be separated and classified according to physical properties such as particle size, shape, and density, laying the foundation for subsequent treatment. Although the baler does not directly participate in the screening process, it serves as a key piece of equipment that connects screening with subsequent disposal. It plays an irreplaceable role in enhancing waste treatment efficiency, optimizing resource utilization, and reducing environmental impact. The baler’s role in different post-screening scenarios includes:
1. Landfill Applications
Horizontal Balers
a. Reducing landfill volume and extending landfill lifespan:
In landfill operations, waste compressed into bales by balers can reduce volume by two-thirds or more. This means that landfills of the same capacity can accommodate more waste, effectively extending their service life. For example, in a large city landfill, introducing a baler can reduce space usage by approximately 20% annually, saving significant land resources and construction costs.
b. Reducing leachate generation:
Loose waste contains more air, which promotes anaerobic fermentation during landfilling and results in large amounts of leachate. Compressed waste bales contain significantly less air, slowing the fermentation process and reducing leachate production. This reduction lowers both the cost and complexity of leachate treatment and decreases the risk of soil and groundwater contamination.
c. Facilitating landfill operations and site management:
Uniform bales make stacking and compacting easier during landfill operations, improving efficiency. Neatly stacked bales also help in daily management and monitoring, such as tracking waste settlement and maintaining biogas collection systems.
2. Waste Incineration Applications
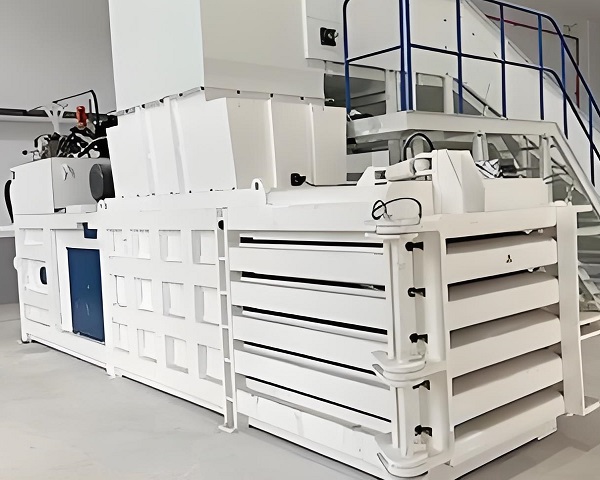

Horizontal Balers
a. Enhancing incineration efficiency and stability:
Compressed bales have a uniform density and burn more thoroughly in incinerators. Compared to loose waste, they allow for more controlled combustion, improving furnace thermal efficiency and power generation. For instance, in waste-to-energy plants, baled waste can improve combustion efficiency by 10%–15%, with corresponding increases in power output.
b. Reducing emissions of flue gas pollutants:
Better combustion of baled waste reduces emissions of pollutants like carbon monoxide and soot. Additionally, bales minimize fly ash caused by waste movement, decreasing the burden on gas purification systems, cutting treatment costs, and improving compliance with emission standards.
c. Reducing wear on incineration equipment:
Loose waste often contains hard objects like stones and metals that damage incinerator components. Baling compresses the waste and may involve pre-treatment such as magnetic separation, resulting in more uniform content and reducing direct impacts on incinerator parts. This prolongs equipment life and lowers maintenance costs.
3. Resource Recovery Applications
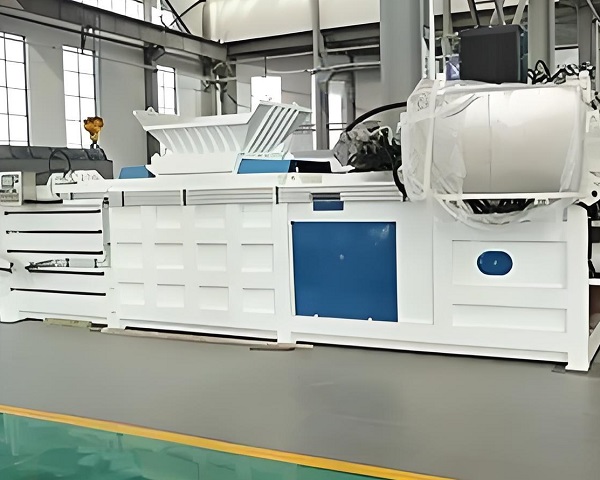

Horizontal Balers
a. Facilitating material transport and storage:
For recyclable materials like plastic, metal, and paper, baling enhances transportability and storability. Regular-shaped bales are less prone to scattering during transport and can be neatly stacked, improving warehouse space efficiency. The reduced contact area with air also minimizes oxidation and moisture damage, preserving material value.
b. Improving resource processing efficiency:
Baled materials can be directly fed into processing equipment for plastic pelletizing, metal smelting, paper recycling, etc., reducing sorting and handling time and labor. Their uniformity also ensures stable processing, boosting equipment efficiency and product quality. For example, in plastic recycling plants, baled plastic waste can increase production efficiency by over 20% and improve product qualification rates.
c. Promoting the development of the recycling industry chain:
Baling makes resource recovery more standardized and efficient, attracting more enterprises to the recycling industry. This helps form a closed-loop industrial chain—from collection, screening, and baling to resource processing and reuse—enhancing the economic and social value of recycling.
4. Optimizing the Entire Waste Treatment Process
a. Increasing overall treatment efficiency:
As a critical component in the waste management process, the baler works in close coordination with screening, transportation, and downstream processing equipment, enabling continuous and automated waste handling. It compresses screened waste quickly, reducing delays in each stage. For example, at a large treatment facility, introducing automated balers increased waste processing efficiency by over 30%, better meeting urban demands.
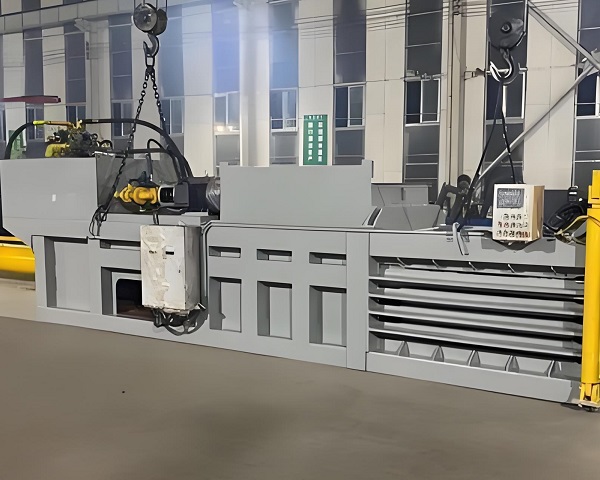

Horizontal Balers
b. Reducing overall treatment costs:
While balers require investment and operational costs, they significantly lower the total cost over the full lifecycle. By reducing waste volume, they lower transportation costs; by reducing landfill use and leachate generation, they cut related expenses; and by boosting incineration and recycling efficiency, they generate economic returns. Automation also reduces labor costs and equipment stability lowers maintenance costs. Overall, balers can reduce comprehensive waste treatment costs by 15%–20%.
c. Enhancing environmental benefits:
Balers help reduce pollution during treatment. They prevent waste spillage and odor during transport and storage; they lower emissions from landfill leachate and incineration flue gas; and they boost resource recovery rates, reducing environmental pressure from resource extraction and waste discharge. These contributions make waste management more eco-friendly and aligned with sustainable development goals.
Balers play a pivotal role in post-screening waste management. By compacting loose waste, they solve numerous issues and significantly contribute to landfill, incineration, and resource recovery processes. They optimize the entire treatment flow, improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance environmental performance. With continuous technological advancements, balers will keep evolving, offering stronger support for reducing, reusing, and safely disposing of waste—ultimately helping to build a greener, more sustainable waste management system.