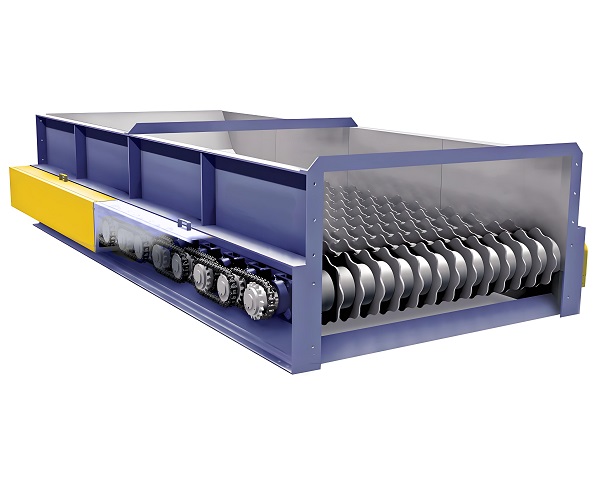
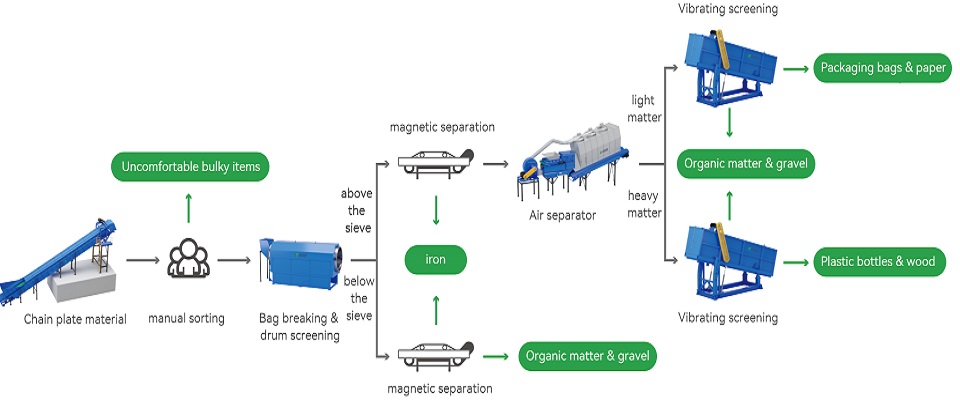
A Trommel Screen is a rotary drum screening machine widely used in waste processing, mining, and construction industries. It efficiently separates materials by ......
What is the Iron Remover
Iron Remover is a device used to automatically remove ferromagnetic impurities from raw materials. It is widely used in material conveying systems in industries such as cement, electricity, mining, ceramics, glass, chemicals, food, and plastics. Its main function is to protect downstream equipment (such as crushers, mills, conveyors, etc.) from damage by iron impurities, ensure the safe operation of equipment, and improve product purity and quality.
The working principle of the iron remover is based on magnetic separation technology. The equipment is usually installed above the conveyor belt, feed pipe or feed port. When the material containing iron impurities passes through, the strong magnetic field will absorb the iron debris, such as screws, nails, iron sheets, etc., and separate them from the raw materials. Some automatic iron removers (such as self-unloading permanent magnetic iron removers) are also equipped with belts or chain structures, which can realize the automatic unloading function, save manual cleaning time, and improve work efficiency.
According to different magnetic sources, iron removers are mainly divided into two types: permanent magnetic and electromagnetic. Permanent magnetic iron removers use high-performance NdFeB magnets, which have stable magnetic field strength, do not require external power supply, are energy-saving and environmentally friendly, and are suitable for continuous working environments; while electromagnetic iron removers generate strong magnetic fields through energized coils, have strong magnetic force and strong penetration, and are suitable for thick layers, high-speed materials or occasions with high iron content. Some electromagnetic iron removers are also equipped with automatic cooling systems (air cooling, water cooling or oil cooling) to extend service life and ensure safe operation.
Iron removers also have a variety of structural forms such as dry, wet, pipeline, hanging, and plate types, which can be flexibly selected according to material properties and installation conditions. Some high-end equipment also has an intelligent control system that can remotely monitor the operating status and cleaning frequency to realize the digitalization and automation management of the production process.
Iron removers are an auxiliary equipment with simple structure, strong adaptability, and stable operation. They can effectively prevent iron impurities from damaging the equipment and improve the quality of raw materials. They are an indispensable and important part of modern production lines, especially suitable for industrial scenarios with high cleanliness and high safety requirements.
Operating principle of Iron Remover
Iron Remover is a device used to remove ferromagnetic impurities from various materials. It is widely used in mining, metallurgy, building materials, ceramics, electricity, food, chemical industry, recycling and other industries. During the material transportation or processing process, if magnetic impurities such as iron nails, iron blocks, screws, etc. are mixed in, it will not only affect the product quality, but also may damage downstream equipment. Iron remover is designed to solve this problem. Its working principle is based on electromagnetic or permanent magnetic technology, combined with the conveying system, to achieve efficient adsorption and removal of ferromagnetic materials.
The basic working principle of iron remover is: when the material containing iron impurities passes through the magnetic field area of the iron remover, the magnetic material is adsorbed under the action of the magnetic field force, while the non-magnetic material passes smoothly. Common iron removers include permanent magnetic iron removers and electromagnetic iron removers. Permanent magnetic iron removers use high-performance rare earth magnets to generate a strong magnetic field without the need for an external power supply. They are suitable for continuous operation and low maintenance. Electromagnetic iron removers generate a strong magnetic field through an energized coil, and its magnetic force can be adjusted. They are suitable for scenes with higher requirements for iron removal accuracy or larger material particle size and weaker magnetism.
For the self-unloading iron remover, the main body of the iron remover is installed above the conveyor belt. Through the self-unloading belt system on the conveyor belt, the adsorbed iron impurities are automatically taken away from the main flow of the material and fall into the iron collecting box to realize the automatic iron removal function. The manual iron removal type iron remover requires regular manual cleaning of the adsorbed iron impurities, which is suitable for working conditions with small workload or discontinuous operation.
In wet working environments, liquid pipeline iron removers or electromagnetic slurry iron removers can also be used. These devices are installed in the pipelines through which the materials flow, and the flowing liquid or slurry is treated for online iron removal to avoid pipeline blockage and equipment corrosion.
With its high efficiency, energy saving, safety and stable operation characteristics, the iron remover effectively guarantees the safety and efficiency of the production system, and is one of the key equipment in modern industrial material transportation and processing systems.
Advantages and features of Iron Remover
Iron Remover is a special equipment used to remove ferromagnetic impurities from raw materials. Its main function is to ensure the safety of downstream equipment, improve product purity, optimize process flow, and improve overall production efficiency. The following is a detailed description of its characteristics and advantages:
1. The iron remover has strong magnetic force and efficient iron removal ability. Whether it is a permanent magnet or an electromagnetic coil, its magnetic field strength can meet the iron removal needs in different application scenarios. The high magnetic field can effectively capture small to large iron impurities in powdered, granular, blocky and other raw materials to ensure the purity of the raw materials, especially suitable for fine production processes with extremely high impurity requirements.
2. The iron remover has a variety of structural forms and installation methods, including hanging, pipeline, self-unloading, permanent magnetic drum, etc., which can be flexibly adapted to various conveying equipment and process layouts. Users can choose the most suitable model according to material characteristics, processing volume and on-site space to meet personalized production needs.
3. Modern iron removers generally use automatic unloading or online cleaning functions, which greatly reduces the frequency of manual intervention and improves the continuity and safety of operation. For example, the self-unloading iron remover uses a belt to automatically discharge the adsorbed iron debris, achieving unattended and efficient operation. Some high-end models can also realize PLC automatic control, integrated into the entire production line, and improve the level of automation.
4. The iron remover has the advantages of simple structure, stable operation and convenient maintenance. The equipment has a low failure rate, a long replacement cycle for wearing parts, and low operating energy consumption, especially the permanent magnet series products, which have stable and lasting magnetic force, do not require additional power supply, have extremely low operating costs, and are environmentally friendly and energy-saving.
5. Today, as green manufacturing and resource recycling are increasingly valued, iron removers also play an important role in solid waste treatment, renewable resource sorting and other fields, effectively realizing metal recycling and secondary utilization of resources, and creating added value for enterprises.
Iron Remover has become an indispensable and important equipment for modern industrial production with its high iron removal efficiency, strong adaptability, high degree of automation, simple maintenance, energy saving and environmental protection.
Technical Parameter Table of Iron Remover
| Model | Magnetic Field Strength (mT) | Applicable Belt Width (mm) | Rated Suspension Height (mm) | Capacity (t/h) | Power (kW) | Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCYD-5 | 60 | 500 | 150 | 60 | 1.5 | 950 |
| RCYD-6 | 70 | 600 | 180 | 90 | 2.2 | 1150 |
| RCYD-8 | 70 | 800 | 200 | 120 | 2.2 | 1400 |
| RCYD-10 | 75 | 1000 | 250 | 150 | 3.0 | 1750 |
| RCYD-12 | 75 | 1200 | 300 | 200 | 4.0 | 2100 |
| RCYD-14 | 80 | 1400 | 350 | 260 | 4.5 | 2500 |
If you have any special requirements, we will customize according to your special needs.
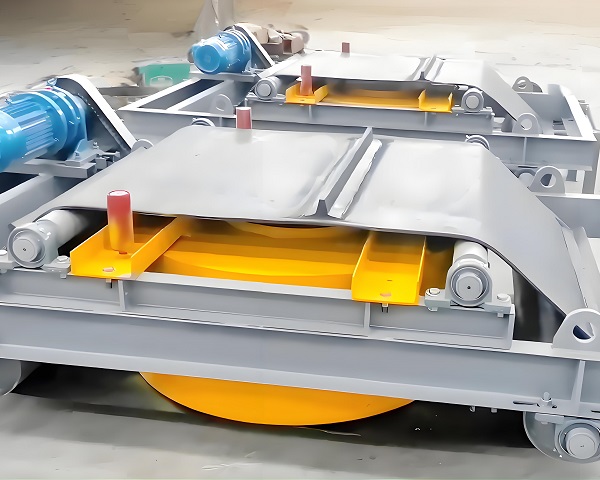
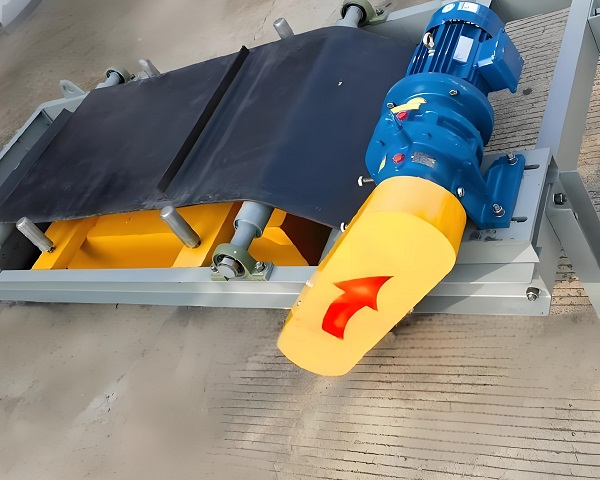
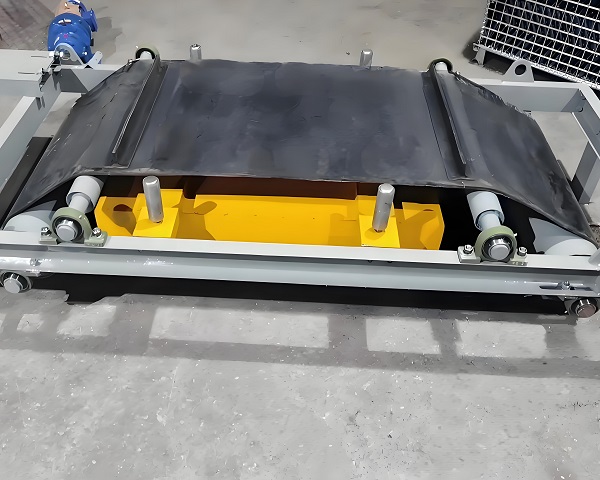
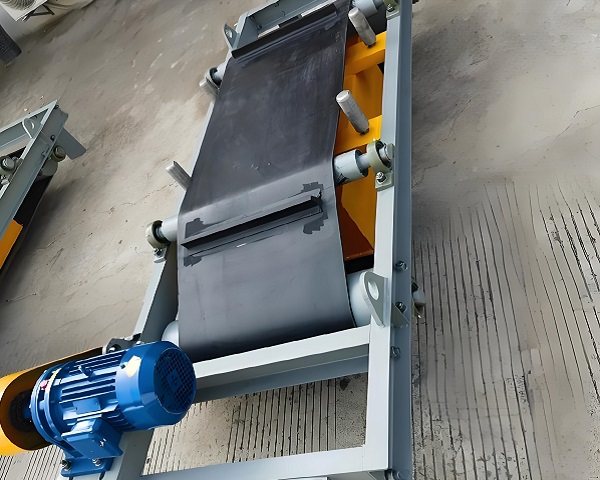
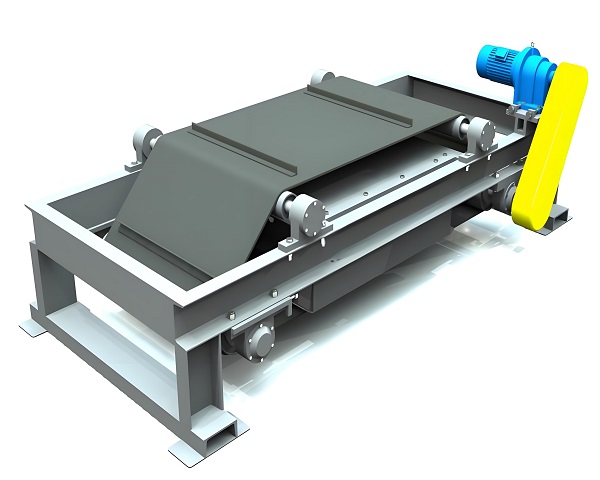
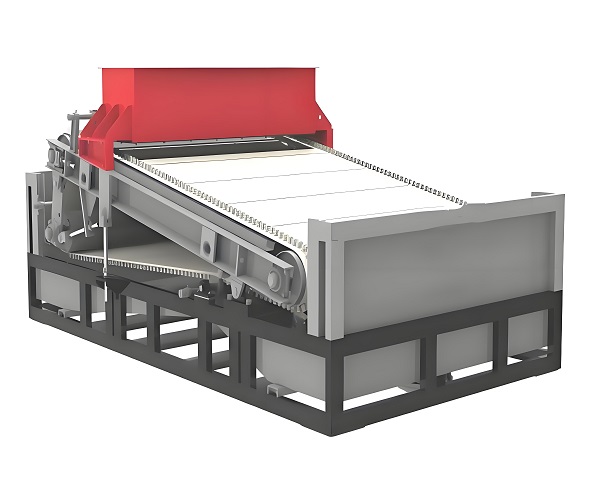
Product Picture Display of Iron Remover
FAQ about Iron Remover
>What are the different types of Iron Removers?
There are several types. Permanent magnet iron removers use magnets like ferrite or neodymium magnets to create a constant magnetic field. They are cost - effective and suitable for applications where a stable, moderate - strength magnetic field suffices, such as in small - scale food processing to remove iron contaminants. Electromagnetic iron removers rely on an electric current passing through a coil to generate a magnetic field. The advantage is that the magnetic field strength can be adjusted by varying the current, making them ideal for industrial applications with diverse iron - separation needs. Additionally, there are self - cleaning iron removers, which automatically clear accumulated iron, and manual - cleaning types, where operators need to remove the collected iron periodically.
>Where are Iron Removers commonly used?
Iron removers find wide applications across multiple industries. In the mining industry, they are used to separate iron - rich ores from gangue materials, improving the purity of the extracted minerals. In the food and beverage industry, they prevent iron contaminants from entering products, ensuring food safety. For example, in flour mills, iron removers keep iron particles out of the flour. In recycling plants, iron removers help in separating iron - based metals from mixed waste, facilitating recycling efforts. They are also crucial in power plants, protecting coal - handling equipment from iron - related wear and tear.
>Can an Iron Remover be used for water treatment?
Yes, iron removers are widely used in water treatment. Excessive iron in water can cause problems like staining of fixtures, a metallic taste, and corrosion of pipes. In water treatment systems, iron removers use methods such as oxidation and filtration. For example, in an aeration - based iron removal system, air is introduced to the water to oxidize soluble iron (ferrous iron) into insoluble iron (ferric iron). The iron then precipitates out and can be removed by filtration. Magnetic iron removal systems for water work by attracting iron particles with a magnetic field and separating them from the water flow.
>How do you choose the right Iron Remover for a specific application?
When choosing an iron remover, several factors need consideration. First, assess the nature of the material to be processed. If it's a fine - grained powder, a high - intensity magnetic separator might be required. Second, consider the volume of material to be processed. Larger - scale operations need iron removers with higher throughput capacities. Third, think about the magnetic properties of the iron contaminants. Strongly magnetic iron requires less powerful iron removers compared to weakly magnetic iron oxides. Also, take into account the operating environment, such as temperature, humidity, and space limitations.
>What is the difference between a permanent magnet and an electromagnetic Iron Remover?
Permanent magnet iron removers have a fixed magnetic field strength determined by the properties of the permanent magnet material. They are relatively simple in design, require no external power source to generate the magnetic field, and are cost - effective for applications where a constant magnetic field is sufficient. In contrast, electromagnetic iron removers use an electric current to generate a magnetic field. This allows for adjustable magnetic field strength, which is beneficial when dealing with materials having different magnetic susceptibilities or when the separation requirements change frequently. However, they consume electricity and are generally more complex and costly to install and maintain.
>How do you maintain an Iron Remover?
Regular maintenance is crucial for the efficient operation of an iron remover. For permanent magnet iron removers, periodically check the magnets for any signs of damage or weakening. Clean the magnetic surfaces to remove accumulated iron particles, as this can reduce the magnetic field's effectiveness. For electromagnetic iron removers, in addition to cleaning, inspect the electrical components, such as wires, coils, and switches, for wear and tear. Ensure proper cooling if the electromagnetic unit generates heat during operation. Also, check the conveyor belts or other moving parts (if applicable) for signs of wear and replace them as needed.
>What are the safety precautions when using an Iron Remover?
When operating an iron remover, safety should be a top priority. Keep hands and other body parts away from moving parts, such as conveyor belts and magnetic drums. For electromagnetic iron removers, follow proper electrical safety procedures, including turning off the power before maintenance and ensuring proper grounding. Since iron removers can generate strong magnetic fields, keep magnetic - sensitive devices, such as pacemakers and credit cards, away from the machine. Also, use appropriate personal protective equipment, like safety glasses to protect against flying particles when removing accumulated iron.
>Can an Iron Remover remove other metals besides iron?
While iron removers are primarily designed for iron, they can also remove some other ferromagnetic metals. Metals like nickel and cobalt, which are also ferromagnetic, will be attracted to the magnetic field of an iron remover and can be separated in a similar way to iron. However, non - ferromagnetic metals such as aluminum, copper, and zinc will not be affected by the magnetic field of a typical iron remover. In some cases, modified iron removers or additional separation processes may be used to target a wider range of metals.
>What is the capacity of an Iron Remover?
The capacity of an iron remover varies widely depending on its type and design. Small - scale bench - top iron removers used in laboratories or small - scale production may have a capacity to process a few kilograms or liters of material per hour. Industrial - scale iron removers, on the other hand, can handle large volumes. For example, a belt - type iron remover in a coal - handling plant may be able to process hundreds of tons of coal per hour. The capacity is determined by factors such as the size of the magnetic field, the speed of the conveyor belt (if applicable), and the efficiency of the separation mechanism.
>How does the cost of an Iron Remover vary?
The cost of an iron remover is influenced by multiple factors. The type of iron remover is a significant factor. Electromagnetic iron removers, with their more complex electrical components and adjustable features, are generally more expensive than permanent magnet iron removers. The size and capacity of the iron remover also play a role. Larger, high - capacity iron removers cost more due to the increased materials and engineering required. The quality of components, such as the use of high - grade magnets or durable conveyor belts, can raise the cost. Additionally, custom - designed iron removers, tailored to specific applications, are likely to be more expensive than standard models.
>Can an Iron Remover be integrated into an existing production line?
Yes, iron removers can often be integrated into existing production lines. For example, in a food - processing line, a magnetic belt - type iron remover can be installed above the conveyor belt that transports the food product. In a mining operation, an iron remover can be added to the ore - processing conveyor system. However, when integrating, it's important to ensure that the iron remover's size, capacity, and operating parameters are compatible with the existing line. This may involve making adjustments to the conveyor speed, the height of the iron remover above the material flow, and ensuring proper electrical connections for electromagnetic models.
>What are the signs that indicate an Iron Remover is not working properly?
If an iron remover is not working properly, there are several tell - tale signs. In a production line, an increase in iron - related damage to downstream equipment, such as jamming of crushers or wear on conveyor belts, may indicate that the iron remover is not effectively removing iron. In water treatment, a return of iron - related problems like staining or a metallic taste in the water can suggest issues with the iron remover. Visually, if an iron remover is supposed to collect iron particles but has very little or no accumulation, it may not be functioning correctly. For electromagnetic iron removers, unusual noises or overheating of the electrical components can also be signs of malfunction.
>How long does an Iron Remover typically last?
The lifespan of an iron remover depends on various factors. With proper maintenance, a well - built iron remover can last for many years. High - quality permanent magnet iron removers can have a lifespan of 10 - 15 years or more, as the permanent magnets are generally durable and not prone to rapid degradation. Electromagnetic iron removers may have a slightly shorter lifespan, typically 8 - 12 years, due to the potential wear and tear of electrical components. However, if an iron remover is used in harsh environments, such as in a highly corrosive industrial setting or with excessive dust, its lifespan may be significantly reduced.
>Are there any environmental considerations when using an Iron Remover?
When using an iron remover, there are some environmental aspects to consider. For electromagnetic iron removers, energy consumption is a factor. Choosing energy - efficient models can help reduce the overall energy footprint. In industrial applications, the disposal of the separated iron and any associated contaminants needs to be managed properly. If the removed iron is contaminated with harmful substances, it should be treated or disposed of in accordance with environmental regulations. Additionally, the materials used in the construction of the iron remover, such as the housing and conveyor belts, should be chosen with recyclability in mind to minimize waste at the end of the machine's life.
>Can an Iron Remover be used for fine - particle iron removal?
Yes, there are iron removers specifically designed for fine - particle iron removal. High - intensity magnetic separators are often used in such cases. These separators generate a very strong magnetic field that can attract even tiny iron particles. In industries like mineral processing, where fine - grained iron ores need to be separated from other minerals, high - intensity magnetic iron removers are employed. In water treatment for removing fine iron particles, specialized filters in combination with magnetic fields can effectively capture and remove these particles, ensuring high - quality water output.
>What is the role of an Iron Remover in a recycling process?
In a recycling process, an iron remover plays a crucial role. It helps in separating iron - based metals from mixed waste materials. This separation is important as it allows for the recycling of iron - based metals, reducing the need for virgin metal extraction. For example, in a municipal solid waste recycling facility, an iron remover can identify and extract iron - containing items such as cans, metal scraps, and old appliances. By separating these iron - based materials, it becomes easier to process and recycle them, contributing to a more sustainable and resource - efficient recycling system.
>How do you test the effectiveness of an Iron Remover?
To test the effectiveness of an iron remover, one can use several methods. In a laboratory setting, a sample of the material to be processed can be passed through the iron remover, and then analyzed for remaining iron content using techniques such as spectroscopy or magnetic susceptibility measurements. In an industrial setting, visual inspections can be made of downstream equipment to check for signs of iron - related damage. Another method is to measure the amount of iron collected by the iron remover over a period of time. If the iron remover is not collecting an appropriate amount of iron considering the expected iron content in the incoming material, its effectiveness may be in question.
>Are there any new technologies or advancements in Iron Remover design?
There are continuous advancements in iron remover design. New magnetic materials are being developed that offer higher magnetic strength and better stability, improving the performance of iron removers. Some modern iron removers are equipped with smart sensors and control systems. These can automatically adjust the magnetic field strength based on the iron content in the incoming material, optimizing the separation process. There are also efforts to make iron removers more compact and energy - efficient, reducing their footprint and operating costs. Additionally, improved corrosion - resistant materials are being used to enhance the durability of iron removers in harsh environments.